Choosing the ideal engagement ring remains a captivating debate, with natural diamonds and lab-grown diamonds both offering unique attributes that appeal to diverse buyers. In this article, we delve into the reasons why opting for a natural diamond ring surpasses choosing a lab-grown one for your dream engagement ring. By understanding the distinctions between these options, you can make a well-informed decision that aligns with your values and desires.
From the controlled environments of laboratories, lab-grown diamonds, also known as synthetic or man-made diamonds, emulate the natural diamond formation process through advanced technological methods. On the other hand, natural diamonds undergo a billion-year journey beneath the Earth's surface, resulting in unparalleled gems of exceptional quality. Our exploration will highlight the significance of rarity, investment value, environmental impact, and expert verification in differentiating these two types of diamonds, assisting you in choosing the perfect symbol of your love.
What is a Lab-Grown Diamond?
A lab-grown diamond, also known as a synthetic or man-made diamond, is a diamond produced in a controlled environment in a laboratory setting. Unlike natural diamonds that are formed over billions of years under the Earth's surface, lab-grown diamonds are created through advanced technological processes that mimic the conditions in which diamonds naturally develop. These processes involve two primary methods: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT).
In the CVD method, a diamond seed is placed in a chamber filled with carbon-rich gases, and upon exposure to extreme heat, the gases break down, causing carbon atoms to adhere and crystallize on the seed, eventually forming a larger diamond. In the HPHT method, carbon is subjected to high pressure and temperature to induce diamond formation. The result is a diamond that shares the same physical and chemical properties as a natural diamond but is produced in a shorter time frame under controlled conditions.
Lab-Grown Diamond Rings have gained popularity as an alternative to natural diamonds due to factors such as ethical concerns, cost-effectiveness, and environmental concerns. However, it's essential for consumers to be aware of the differences between lab-grown and natural diamonds and make an informed decision based on their individual preferences and values. This article will explain the difference between the two so you can make the right decision for you.
Rarity and Finite Nature
The rarity and finite nature of natural diamonds play a crucial role in shaping their value and desirability in the market. The Natural Diamond Council (NDC) highlights the authenticity of natural diamonds' rarity when differentiating them from lab-grown counterparts. Natural diamonds take billions of years to form deep within the Earth's crust under intense pressure and heat—this lengthy and natural process results in gems of exceptional quality and uniqueness. In contrast, lab-grown diamonds can be produced in a controlled environment, allowing for mass production without the constraints of rarity.
Additionally, natural diamonds are becoming scarcer by the day as no significant new deposits have been discovered in approximately 30 years. This scarcity drives the appreciation of natural diamond prices over time, making them a coveted investment for collectors and investors alike. The limited supply of natural diamonds, combined with their timeless appeal, contributes to their enduring value and status as a billion-year-old precious gem.
Timeless Value and Investment
The natural scarcity of diamonds contributes to their enduring value and investment potential. Aged beneath the Earth's surface, natural diamonds are rare and finite resources, making their supply limited. This rarity has led to a consistent appreciation in their value over time, making them a sought-after investment choice.
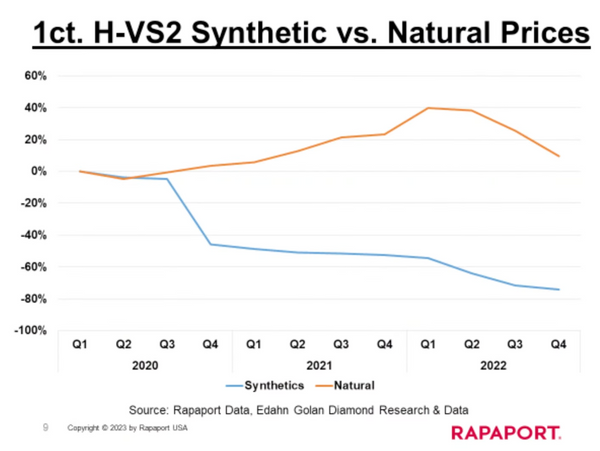
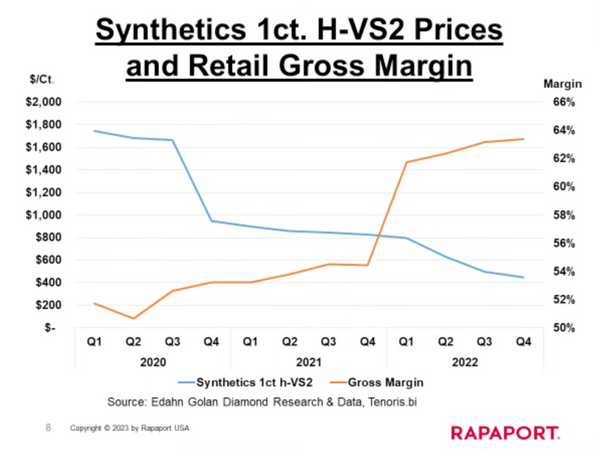
In contrast, lab-grown diamond engagement rings are manufactured, leading to higher production rates and a more abundant supply. As stated in Martin Rapaport’s Full Disclosure Request, “Man-Made Diamonds do not appreciate in value like natural diamonds because they can be created in unlimited quantities and are not subject to the same supply limitations as natural diamonds.”
Since 2020, synthetic diamond prices have decreased by almost 80%, meaning they do not retain their value. While the volume of synthetic diamonds on the market is increasing, leading to a decrease in wholesale prices, retailers continue to drive up their profit margins, charging 2.5-3x or more for synthetic diamonds over their actual cost without disclosing important information to customers.
Without the inherent scarcity of natural diamonds, lab-grown diamonds do not exhibit the same long-term investment potential. The increasing availability and potential for reduced production costs impact their value over time, distinguishing natural diamonds as a superior option for those seeking a valuable and timeless asset.

Environmental Impact
Natural diamonds can be considered more environmentally friendly than lab-grown diamonds due to their responsible sourcing and reduced energy consumption. Diamond mining companies have made significant strides in adopting sustainable practices, minimizing their environmental impact, and protecting local ecosystems and wildlife habitats. For instance, modern diamond mining operations follow strict guidelines for waste management, land rehabilitation, and reforestation efforts, contributing to a greener diamond extraction process. Moreover, many mining companies now utilize renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to further reduce their carbon footprint during the extraction process.
In contrast, lab-grown diamonds are produced in controlled environments through energy-intensive processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) methods. These methods require a substantial amount of energy, often sourced from non-renewable fossil fuels, contributing to a higher carbon footprint than natural diamonds.
It is estimated that most synthetic diamond growers require 250 - 750 kilowatt hours (kWh) to produce a rough carat. And even more energy is required during the cutting and polishing process. For reference, the average US household uses about 30 kilowatt hours per day. The energy used to produce a rough lab diamond could power up to 25 US households or charge up to 15 Model 3 Teslas.
Additionally, lab-grown diamond production can be water-intensive, necessitating careful management of water resources during cooling processes and equipment maintenance.
Expert Verification and Certification
Distinguishing between lab-grown diamond engagement rings and natural diamonds can indeed be a daunting task for the untrained eye. However, reputable gemological laboratories like the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) have played pivotal roles in developing reliable methods to differentiate between the two types of diamonds.
The GIA, a world-renowned authority in gemology, has implemented advanced techniques to analyze diamonds and determine their origin. Their team of skilled gemologists utilizes cutting-edge technology and expert knowledge to examine the unique features of each diamond.
The GIA utilizes advanced spectroscopy techniques, such as infrared and ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy, to analyze diamonds' unique features and trace elements. These techniques can reveal subtle differences between lab-grown and natural diamonds, such as the presence of certain elements or the type of growth patterns. In addition, the GIA examines the diamond's internal characteristics, known as inclusions, which can provide valuable clues about its origin.
Apart from spectroscopy, the GIA also employs advanced equipment, including DiamondView and DiamondSure, to assess diamonds' fluorescence and phosphorescence. These tools aid in detecting potential indicators of lab-grown diamonds, as they may exhibit different fluorescence patterns compared to natural diamonds.
While advanced laboratory testing is essential for accurate identification, there are some visual cues that can hint at a diamond's origin. For instance, some lab-grown diamonds may display unique growth patterns or patterns created during the cutting process, which can be different from those found in natural diamonds. However, these visual distinctions are not always definitive and can be challenging to detect without expert training and equipment.
Moreover, the FTC, as a consumer protection agency, ensures that accurate and transparent information is provided to buyers. They have published guidelines on advertising and marketing practices in the diamond industry, including the proper disclosure of whether a diamond is natural or lab-grown. This helps consumers make informed decisions and ensures that they can confidently verify the authenticity of their precious gem.

Timeless Beauty of Antique and Vintage Diamonds
For those seeking a unique engagement ring, antique diamond rings offer an exquisite story. Antique diamond rings possess historical significance and craftsmanship that can't be replicated, making them a cherished heirloom for generations to come. These diamonds carry captivating stories, having witnessed and symbolized enduring love throughout history. For example, a vintage diamond engagement ring from the Art Deco era showcases intricate geometric designs and bold shapes, reflecting the artistic spirit of the time. Each antique diamond tells a tale of romance and sentiment, infusing the ring with a sense of nostalgia and charm that simply cannot be matched by lab-grown diamonds.
Furthermore, antique and vintage diamonds often boast unique characteristics, such as Old European or Old Mine cuts, which are not commonly found in modern diamonds. These vintage cuts exude a captivating brilliance and fire, captivating the beholder with their distinctive beauty. Unlike lab-grown diamonds, which are typically cut using modern techniques, the vintage cuts offer a glimpse into the elegance and artistry of bygone eras. Each facet and facet arrangement in these antique diamonds is a testament to the skills of master craftsmen, who carefully shaped these gems by hand. The rarity and artistry of these cuts add to the allure of antique diamond rings, making them an unparalleled choice for those seeking a truly exceptional and meaningful engagement ring.
Conclusion
In conclusion, as you embark on the journey of selecting your dream engagement ring, the comparison between natural diamonds and lab-grown diamonds reveals compelling insights. While lab-grown diamonds offer cost-effectiveness and potential eco-friendliness, the allure of natural diamonds lies in their unmatched rarity, investment value, sustainability, and emotional significance.
These billion-year-old treasures, formed deep within the Earth's crust, carry with them a profound connection to the Earth's history, making them more than just exquisite gems—they are symbols of enduring love and commitment. As you embark on this momentous decision, may the knowledge presented here guide you in making an informed and meaningful choice—a choice that reflects not only your commitment to your partner but also your commitment to sustainability, investment value, and the enduring beauty of nature's most precious gift.

Sources:
IGS (International Gem Society). "Lab-Grown Diamond Production Methods." International Gem Society, https://www.gemsociety.org/article/lab-grown-diamond-production-methods/.
Forbes. "Lab-Grown or Natural Diamonds? The Choice Is Getting Clearer for Consumers and Retailers." Forbes, 14 Feb. 2021, https://www.forbes.com/sites/pamdanziger/2021/02/14/lab-grown-or-natural-diamonds-the-choice-is-getting-clearer-for-consumers-and-retailers/?sh=4d89788362f9.
Cape Town Diamond Museum. "The Fascinating History of Diamond Cutting." Cape Town Diamond Museum, 23 Oct. 2019, https://www.capetowndiamondmuseum.org/blog/2019/10/the-fascinating-history-of-diamond-cutting/.
FTC (Federal Trade Commission). "Many Facets: Advertising Diamonds' Clarity." Federal Trade Commission, 7 May 2019, https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/blog/2019/05/many-facets-advertising-diamonds-clarity
GIA (Gemological Institute of America). "The Difference Between Natural and Laboratory-Grown Diamonds." GIA, https://www.gia.edu/gia-news-research/difference-between-natural-laboratory-grown-diamonds
Kyleroderick. "Lab-Grown Diamonds - Regulators Warn That Some Claims Fail to Fulfill Their Hype." Forbes, 24 Aug. 2019, https://www.forbes.com/sites/kyleroderick/2019/08/24/lab-grown-diamonds--regulators-warn-that-some-claims-fail-to-fulfill-their-hype/?sh=4147342d538e
Kyleroderick. "Lab-Created Diamonds Eco-Friendly?" Forbes, https://www.forbes.com/sites/kyleroderick/2019/08/24/lab-grown-diamonds--regulators-warn-that-some-claims-fail-to-fulfill-their-hype/?sh=4147342d538e/editorial-article/lab-created-diamonds-eco-friendly/#:~:text=Lab%20diamonds%20are%20produced%20in,kWh%20per%20successful%20polished%20ct
GIA (Gemological Institute of America). "How do I identify laboratory-grown diamonds?" GIA, https://www.gia.edu/gia-faq-analysis-grading-identify-laboratory-grown-diamonds
Rapaport. “Introduction - Facts about Synthetics.” Youtube, https://www.youtube.com/watch?reload=9&v=ymOu8buVqfg







